What is renal failure
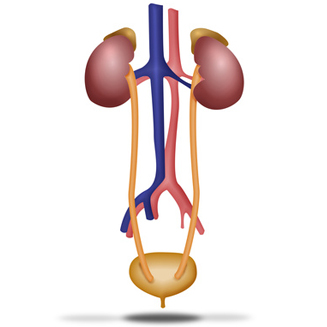 The urinary device is formed by the kidneys, urreters, urinary bladder and urethra and is an end to the formation and elimination of urine.
The urinary device is formed by the kidneys, urreters, urinary bladder and urethra and is an end to the formation and elimination of urine.
The kidneys are two twin organs located in the middle part of the back, on top of the waist, one on each side of the spine, with a bean-shaped and approximate size of a fist.
The ureter is a conduit of about 25 cm. In length and that propulsses the urine from the kidney to the bladder, leaving from here to the outside through the urethra.
Main functions of the kidneys
We can rudely say that the kidneys are the scrubber of our organism and this function is done through the blood filtration that reaches the kidneys by the kidney artery and that It contains toxic substances to debug (urea, creatinine, uric acid, calcium, phosphorus, medications, etc.) and that returns to the circulation already refined through renal vein.
This filtration is carried out through tiny filters called glomeruli. Each kidney has approximately 1,200,000 glomeruli.
Another very important function of the kidneys, is to keep the amount of water controlled, so that it eliminates the excess of water that we drink and avoid eliminating the water we need. In addition, it simultaneously maintains the necessary balance of many components of blood (sodium, potassium, calcium, phosphorus, bicarbonate and other ions) so that the functions of other organs are properly carried out.
The urine that we eliminate is therefore the final result of the previous 3 functions, its composition and volume will vary depending on the different circumstances of the day or the days. In this composition, what we eat, what we drink, the salt we take, if we are taking medications, as we are hydrated etc. And the total volume of urine fundamentally will depend on what we drink, so that drinking about 2 liters, the urine formed would oscillate between 1-1.5 l per day.
In addition, the kidney has other fundamental functions such as:
- Erythropoietin formation (EPO), which stimulates the formation of red blood cells in the bone marrow and whose absence brings anemia.
- is a fundamental regulator of blood pressure by controlling the organism, sodium and voltage regulatory hormones (renin-angiotensin-aldosterone).
- Bone composition, since it is responsible for forming vitamin D active from which we take with the sun and food and contributes along with the regulation of calcium concentration and phosphorus, to the formation of a bone Healthy and quality.
What happens if the kidneys do not work well?
It should be noted, that when we talk about kidney failure, we are talking about an alteration of the function of the 2 kidneys or one in the event that you only have a kidney. Say also, that you can live perfectly with a single kidney, but it is necessary to assume that the only kidney is performing the function of the 2 and therefore may be more predisposed to develop IRC if we do not take care of it.
When the kidneys do not work well, there is an alteration in all the functions that are proper and the clinical and analytical manifestations will depend on the degree of the loss of renal function and if it is an acute or chronic problem.
When acute renal failure (IRA) occurs, its short duration does not usually give rise to all clinical alterations of the lack of kidney function, however, when alterations are prolonged over time, we already talk about an insufficiency Chronic renal (IRC) and in this case progressively the symptoms and analytical alterations of this situation will appear.
Through a simple blood test (urea and creatinine) and urine (sediment and albumina), you can know the degree of alteration of renal function and know if it is acute or chronic kidney failure.
Types of renal insufficiency and prognosis
Great features we can say that kidney failure can be presented in 2 ways: acute and chronic.
- 1.- Acute renal insufficiency (IRA):
The alteration of kidney functions occurs abruptly. The most common clinical manifestations are those related to the 3 main functions, that is, the depurative function, the regulation of the volume of fluids and the regulation of the ion composition.
Therefore, the most usual thing is to urinate little or even stop urinating and therefore there will be fluid retention with the appearance of edema and in the analyzes an increase in urea and creatinine will be observed, as well as an alteration in the ion composition. On some occasions these alterations can become serious and need immediate treatment, even dialysis.
The causes that can trigger this anger are multiple and are more common in patients admitted to a hospital. From medications, olusted contrasts in predisposed people, dehydration by diarrhea, vomiting or excess diuretics, very low blood pressure by serious infections, obstruction at the outlet of urine (calculations, prostate, etc.).
In people not entered, highlighting that one of the drugs that can most often trigger this situation are the anti-inflammatory, which usually use for problems of joint pains for long seasons, having higher risk people who already have alterations of renal and elderly function.
In general, it is a reversible alteration or that usually cures without sequelae once the cause that has produced it has been resolved.
- 2.- Chronic renal failure (IRC):
The kidneys are & ldquo; Diana & rdquo organs; Of many diseases and in fact nephrologists we usually diagnose diseases that have been able to go unnoticed until then, from deepening in the cause of renal failure. Today, the causes that stand out as more frequent IRC triggers are HTA and diabetes mellitus, so that if they are not controlled properly, they can injure the kidneys. Other diseases are: diseases of immunity (nephritis), chronic kidney infections (pyeronephritis), kidney stones and congenital diseases of kidneys and urinary tract.
If, for something, chronic renal failure (IRC) is characterized, it is because of its lack of symptoms until alterations come to very advanced stadiums, where the actions that can be carried out to delay their progress as much as possible, they look much more Limited that if an early diagnosis of the disease will be performed. Even in very advanced phases, the slow and progressive implantation of alterations entails an adaptation of the organism to the changes produced and therefore a lack of manifestations perceived by the patient.
In advanced phases, the usual thing is to find: anemia due to lack of erythropoietin, edema or legs swollen with fluid retention, arterial hypertension (HTA) by poorly regulating the volume of water, sodium and hormones involved, urea and creatinine figures elevated by Lack of filtration; High phosphorus and potassium levels, together with the lack of bicarbonate in blood (acidosis) all by poor regulation in its elimination in urine; Also changes in bone composition, with more fragile and worst quality bones. As we can see, they are all consequences derived from the loss of different functions.
When we talk about IRC, we are defining a situation maintained over time, which is irreversible and generally progressive towards advanced renal failure. The speed of the loss of the function of the kidneys will depend on one side of the cause that has led this situation, but on the other of a series of factors on which we can act so that the evolution is as slow as possible.
A direct consequence of having a kidney failure, is that this fact should always be warned when we are going to prescribe a medication, well because renal function (anti-inflammatory, some antibiotics etc.) worsen because the usual doses have to be worse. Adjust to the degree of renal failure (usually less dose of medication), through tables that all doctors know and have in our consultations. Many medications are eliminated by the kidneys and by reducing the dose we do not diminish its effectiveness, but its side effects. 
Source and more information:
 http://www.alcerrioja.org
http://www.alcerrioja.org
What is hemodialysis?
In hemodialysis, blood is pumped through soft tubes towards a dialysis team. Within the equipment there is a special filter called dialyzer (also called "artificial kidney"). The dialyzer lets the debris and the additional liquid pass, but it retains the important things that the body needs, such as blood cells and nutrients.
Waste and additional liquids are transported towards a cleaning fluid within the dialysis equipment (called "dialisate"), and clean blood flows back towards you. There is only a small amount of blood out of the body at any given time. On average, the process takes four hours. Most people take the treatment three to four times a week. While your hemodialysis treatment is done, you can read, sleep and even watch television.
In order to connect to the dialysis team, you must have access, or entry, to your bloodstream. This is done through a minor surgery, which is usually done on the arm.
This access is permanent while dialysis is being performed.
If dialysis needs to be performed before it is scarred, a temporary access is placed on the neck or groin. Your health care team will teach you how to take care of your access.
What are the types of access in hemodialysis?
There are three types of access in hemodialysis:
Fistula
A fistula is the recommended option for access. It is performed by joining an artery to a close vein under the skin to form a larger blood vessel. This type of access is recommended because it has fewer problems and lasts longer. A fistula should be placed early (several months before starting dialysis), so that it has a lot of time to scar and be ready to use at the moment you start hemodialysis. You must be evaluated by a special doctor, called Vascular Surgeon, at least six months before starting dialysis.
Graft.
If the blood vessels are not suitable for a fistula, a graft can be used. This involves joining an artery and a close vein with a soft and small tube of synthetic material. The graft is totally under the skin.
Catheter
The third type of access, called Catheter .
It is placed in a large vein of the neck or groin. The ends of the tubes are on the skin, out of the body. This type of access is usually used temporarily if a fistula or graft is not ready or if they need repairs. Catheters can be used as permanent access, but only when it is not possible to place a fistula or graft.
What happens after he scar the fistula or graft?
After the fistula or graft has scarred and dialysis begins, you will be placed two needles in the blood vessels each time you take the treatment. Then the needles will be connected to soft plastic tubes. A tube transports the blood from the needle towards the dialyzer (the artificial kidney), where it is cleaned. Clean blood returns to you through the other tube.
What could be some common problems during treatment?
During hemodialysis, water, salt and waste products are eliminated from the body faster than a normal kidney, so you can experience low blood pressure, cramping, nausea, headaches and fatigue , especially in the first weeks before you get used to treatment.
After taking the treatment for a while, you will learn to recognize the first signs of these symptoms. You can also inform your nurse or technician, so that they can do something to be more comfortable or even prevent them from happening.
What function do diet and medications meet in hemodialysis?
Hemodialysis performs a good job by filtering and eliminating waste products and additional liquid, but can not completely replace the function of healthy kidneys to balance important blood substances. That will be done through the medications that you should take and the dietary plan that you must follow.
You and your dietitian will work on a dietary plan based on your general health status, any medication you take and what you and your family like to eat.
An important part of your diet will be limiting the amount of salt you consume. Eating too much salt, take too much liquids or eating the types of incorrect food among treatments can make your dialysis treatment generate discomfort. You can also have serious effects on your health.
Consuming very few calories can also cause you problems, so do not be surprised if your dietitian asks you to eat more than you think should. You must maintain your strength and weight at healthy levels.
Take all your medications as indicated is also very important. You may need to take pills for blood pressure, medications to keep healthy bones and blood and vitamins and iron.
How is my treatment monitored?
You will be held monthly blood tests. These are very important because they allow your health care team to know how well you are and if you need to make any change in your diet, your medications or even the amount of time you spend on the dialysis equipment.
Can I realize the hemodialysis at home?
Many centers also offer hemodialysis at home, which gives it more freedom and control.
To perform your home treatment, your medical condition must be stable. You must prepare your home for the dialysis team and for other equipment; This could involve changes in the pipes and electrical installation of your home. You will also need a career of attention to help you and you will need space to store supplies.
If you are interested in performing dialysis at home, you and your care companion will receive special training on how to perform your treatment safely.
Talk to your health care team to find out if dialysis at home could be the right choice for you. If you are a candidate, your center will arrange for you to receive the equipment and regular supply delivery. The team will continue to carry out an attentive follow-up and will assist you when you attend the center to carry out blood tests and monthly medical check-ups. You will be given a 24-hour care phone number in case you have an emergency.
Are there different types of hemodialysis at home?
In the case of hemodialysis at home, you can choose between three different types of treatment schemes. The options are as follows:
Conventional hemodialysis at home
The treatments are usually done three times a week. On average, each treatment takes about four hours.
Short duration daily hemodialysis
This involves more treatments every week for shorter periods. For example, it could perform six treatments in a week (compared to the three usual treatments). Each treatment will last about 1½ hour to 2½ hours.
Many people consider that their quality of life improves with this type of dialysis because they sleep better and have a major control of blood pressure levels, anemia (low red blood cell count) and blood phosphorus (an important mineral of blood that is essential for cells and bones).
Night hemodialysis (while sleeping)
This involves long and slower treatments that are performed while sleeping, and usually last six to eight hours. Many people sleep better and have better control of blood pressure, anemia and phosphorus in blood with this type of dialysis.
Night hemodialysis can be done at home or in a dialysis center. However, not all centers offer nocturnal hemodialysis as an option. To learn more about this option, consult your health care provider.
Comparison of hemodialysis: at home or in a center
Advantages Disadvantages
In the home
Dialysis is done in the comfort of your own home.
You do not need to travel to a center of electricity and water.
It has more flexibility to choose the time of day to perform dialysis.
You and your dialysis care companion learn how to perform treatments regardless of center staff.
Being able to adapt the treatment program to your life and its schedules: work can give you more independence and control. To save the equipment, a water system (if necessary) and supplies.
You must have enough space in your home
You may increase your dialysis invoices.
You will need a dialysis care companion
Both you and your dialysis care companion should be absent from work or interrupt your usual routine to assist training.
Dialysis center
Trained personnel perform all parts of the treatment. (You may be able to do some things yourself, such as inserting the needles).
Since other people are made dialysis at the same time, it is possible to make friends.
Other people are performed dialysis at the same time, so it has less privacy.
The days and schedules: of the treatment are scheduled by the center.
You must travel to the center at least three times a week.
Is hemodialysis safe?
It has been proven that hemodialysis, either in a center or at home, is effective, reliable and secure.
Some people may be concerned about the transmission of diseases such as AIDS and hepatitis during treatment; However, all the necessary precautions are taken to ensure that this does not happen. If this is concerned, talk to your nephrologist or another member of your health care team.




